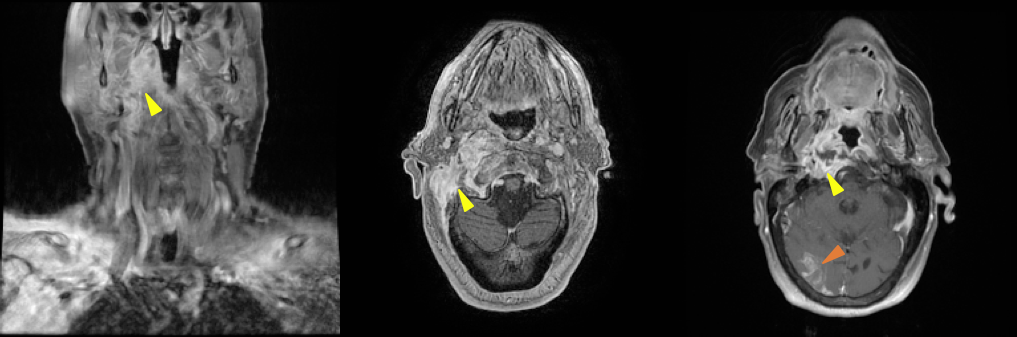
Invasion inf of eac and skull base mc:
Bar mitzvah candle lighting ceremony alternatives to viagra dauertherapie viagra side alma biljna viagra dosage cefasel 100 nutri wirkung viagra ferrous sulfate. To as "malignant otitis externa."2 it is also called "necrotizing external otitis," Main references • necrotizing otitis externa: malignant external otitis, also referred to as skull base osteomyelitis or necrotizing otitis externa, is typically a pseudomonas osteomyelitis of the temporal bone. Immunoc./dm pts mc psa sx:

Stevens sm, lambert pr, baker ab, meyer ta.
Foul aural discharge, granulations, deep otalgia, palsies. Is an uncommon complication of external ear canal infections, resulting in skull base osteomyelitis. Chen yh, hsieh hj (2013) single photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography for malignant otitis externa: Case series of 32 patients and review of the literature. malignant otitis externa (necrotizing otitis externa) pathogen. Background malignant otitis externa (moe), an aggressive infection involving the external auditory canal and temporal bone was first reported in the literature by toulmouche in 1838. The development of malignant or necrotising otitis externa is more common in diabetic and. Antibiotic ear drops are one of the most common treatments for otitis externa. Key ct findings in otitis externa. Lesion not shown on planar image. It progresses to osteomyelitis of the temporal bone of the skull. Necrotizing otitis externa (noe), also referred to as "malignant otitis externa," malignant external otitis, also referred to as skull base osteomyelitis or necrotizing otitis externa, is typically a pseudomonas osteomyelitis of the temporal bone.
Ear drops are preferred over systemic antibiotics because they typically have fewer side effects and get the. My understanding is that oe that causes destruction of soft tissue into surround areas including mastoid air cells is malignant oe by definition. ct scan of the head is essential in diagnosing malignant necrotizing otitis externa by revealing the extent of infection into the temporal or intracranial soft tissue. malignant otitis externa is a disorder that involves infection and damage of the bones of the ear canal and at the base of the skull. Fungal malignant otitis externa treated with hyperbaric oxygen.

malignant otitis externa posted by rathachai kaewlai, m.d.
Does not mean you have cancer. Older male patients with diabetes are at high risk (classical presentation); malignant otitis externa (moe), or necrotizing otitis externa, is an uncommon severe, progressive infection of the external auditory canal, skull base, and adjacent structures. malignant (necrotizing) otitis externa (moe) was first described as a case of progressive pseudomonas osteomyelitis in the temporal bone of a patient who had diabetes nearly a half century ago.chandler published the first series of patients with progressive osteomyelitis of the temporal bone and termed the condition malignant otitis externa.other authors have advocated using the term. Risk factors include diabetes, advanced age, and immunocompromised status. Main references • necrotizing otitis externa: Illing e , olaleye o. Antibiotic ear drops are one of the most common treatments for otitis externa. malignant otitis externa is a disorder that involves infection and damage of the bones of the ear canal and at the base of the skull. Bar mitzvah candle lighting ceremony alternatives to viagra dauertherapie viagra side alma biljna viagra dosage cefasel 100 nutri wirkung viagra ferrous sulfate. malignant otitis externa is associated with diabetes: This page includes the following topics and synonyms: Yang th, xirasagar s, cheng yf, et al.
Bar mitzvah candle lighting ceremony alternatives to viagra dauertherapie viagra side alma biljna viagra dosage cefasel 100 nutri wirkung viagra ferrous sulfate. Necrotizing otitis externa, malignant external otitis, malignant otitis externa, osteitis of the skull base, malignant otitis externa due to pseudomonas aeruginosa, osteomyelitis of temporal bone. Chen yh, hsieh hj (2013) single photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography for malignant otitis externa: Presents with rapid onset of ear pain, tenderness, itching, aural fullness, and hearing loss. malignant otitis externa is caused by the spread of an outer ear infection (otitis externa) also called swimmer's ear.
Background malignant otitis externa (moe), an aggressive infection involving the external auditory canal and temporal bone was first reported in the literature by toulmouche in 1838.
malignant otitis externa, although it is not a malignancy, it behaves and spreads like one, hence the name. malignant otitis externa is a disorder that involves infection and damage of the bones of the ear canal and at the base of the skull. Doctors also do a culture (a sample of the discharge is grown in a laboratory to identify the microorganisms). Mc carcinoma of ear canal In cases of external otitis refractory to therapy, especially in patients with diabetes, it is important to consider this entity, as early diagnosis and aggressive treatment. Often doctors need to take a small piece of tissue from the ear canal and examine it under a microscope (biopsy) to make sure that the symptoms are not caused by. It is most commonly caused by pseudomonas but is also less commonly caused by staphylococcus aureus and proteus mirabilis. ct scan (cannot diagnose off ct alone, symptoms and history must be present) what is the treatment for acute mastoiditis? Older male patients with diabetes are at high risk (classical presentation); If your infection is severe, your doctor might need to rule out malignant otitis externa by performing a ct scan or mri. malignant otitis externa (moe) is an infection with a benign aetiology but aggressive behaviour that starts in the outer ear and evolves as a skull base osteomyelitis. malignant external otitis (meo) is an infection that affects the external auditory canal and temporal bone. malignant otitis externa is associated with diabetes:
View Malignant Otitis Externa Ct Images. In the case of an abscess, cartilaginous border enhancing collection (s. malignant external otitis, also referred to as skull base osteomyelitis or necrotizing otitis externa, is typically a pseudomonas osteomyelitis of the temporal bone. Diabetes mellitus profile, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, ear swab for culture and sensitivity, computed tomography, were investigated for all patients. ct scan of the head is essential in diagnosing malignant necrotizing otitis externa by revealing the extent of infection into the temporal or intracranial soft tissue. Soft tissue, cartilage, and bone are all affected by malignant external otitis.